When preparing their business plan, entrepreneurs sometimes get confused between different terms, especially the difference between a business plan and a financial plan.
Whilst a business plan must include a financial plan, these 2 documents are very different and have separate objectives.
In this article we explain you what are a business plan and a financial plan, their objectives and what are the key differences between them.
What is a Business plan?

A business plan is a long document that contains a detailed description of your business and your strategy. Unlike a pitch deck, a business plan is a Word document and often includes 30 up to 100 pages.
We use business plans to communicate information about a business to third-parties. We often use it when a business needs funding. Debt investors (e.g. banks or venture debt investors) almost always require a business plan as part of a loan application. Instead, equity investors usually ask for a pitch deck.
What should you include in a business plan?
Chances are you will find different definitions online for what you need to include in your business plan. Yet, most interested parties (investors or banks) agree on the different elements that a business plan must include, they are:
- Executive summary: usually a one-pager, this section outlines key information about the company such as a short business overview, operations, location and leadership
- Products and services: a detailed overview of the different products and/or services the company offers including features, benefits to customers and pricing. This section can also include, if relevant, information about the production and manufacturing elements (costs, materials and processes). Also, include here any proprietary technology (e.g. patents) your business might have
- Market analysis: a description of the market including its size and its growth. Here you should also include any information about your competitive environment, especially you position yourself vs. competitors
- Marketing strategy: this section explains how a business acquires and retains its customers. Your acquisition strategy (inbound or outbound for example) as well as your conversion funnel must be clearly explained. If any, you should include here the different marketing campaigns you are running (e.g. paid ads, offline marketing), their goals and historical performance.
- Financial plan: every business plan must include a financial plan. As explained below, a financial plan is the projection in the future of the 3 financial statements. Usually, a financial plan is a 3- to 5-year forecast, depending on the objective of the business plan and the stage the business is in today.
What is a Financial plan?
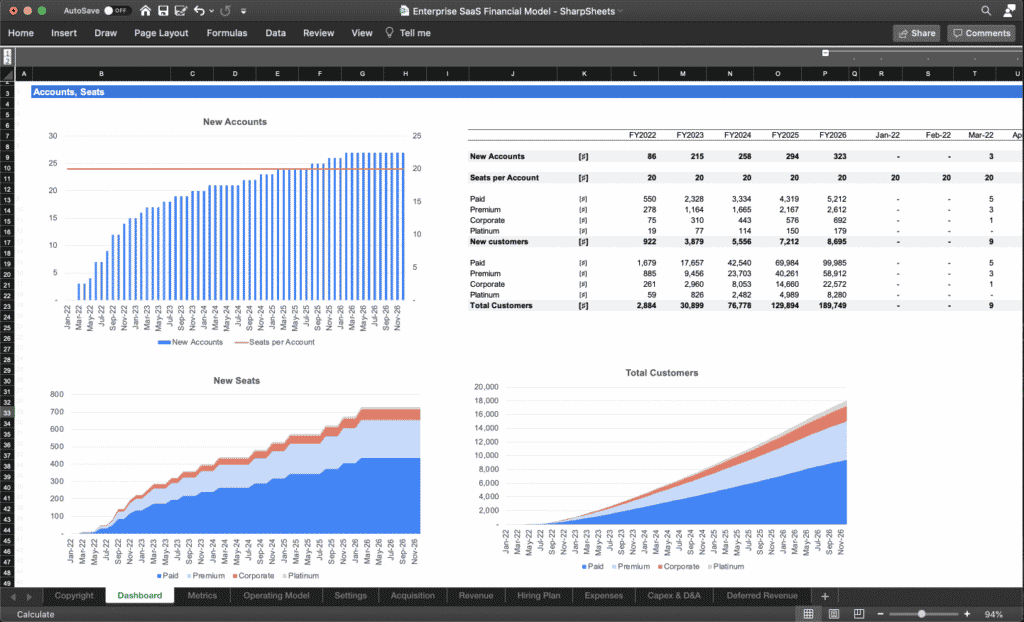
As explained above, a financial plan is an element of every business plan.
A financial plan can take different forms (charts, tables) yet should always at least show the projection over a certain period (3- to 5-year usually) of the 3 financial statements.
A financial plan should also include some historical data (if any). If you have 3 years of historical financial data, include them in there as well. Indeed, investors will want to see how realistic are your projections.
Also, make it clear what are the key assumptions behind your financial forecasts: projecting the future isn’t easy and we often need to make some assumptions. Yet, the more available sources and data points you have to substantiate your projections, the better. Investors appreciate entrepreneurs who are realistic about their projections and understand the opportunities as well as the potentials risks involved. Whenever possible, use historical data and/or industry benchmarks.


