How To Create a EdTech Pitch Deck: Full Guide

UNESCO estimates the global education market at $4.7 Trillion, of which 65% in high-income countries. With only 3% of this spent on technology, it’s no wonder that EdTech has a long way to go. If you are launching your EdTech startup, you will need a rock-solid pitch deck to impress investors, and stand out from the crowd.
In this article we will cover:
The state of EdTech in 2021
Before we dive into the slides you need for your EdTech pitch deck, let’s first have an overview of EdTech today, and more especially:
- How big is EdTech today?
- What are the key trends driving EdTech?
How big is EdTech today?
EdTech only saw $500m venture capital funding in 2010. 10 years later, EdTech totalled $7 billion VC funding, a 15x increase (source: Holon IQ). Interestingly, the bulk of EdTech VC funding is invested in Chinese companies (~50%).
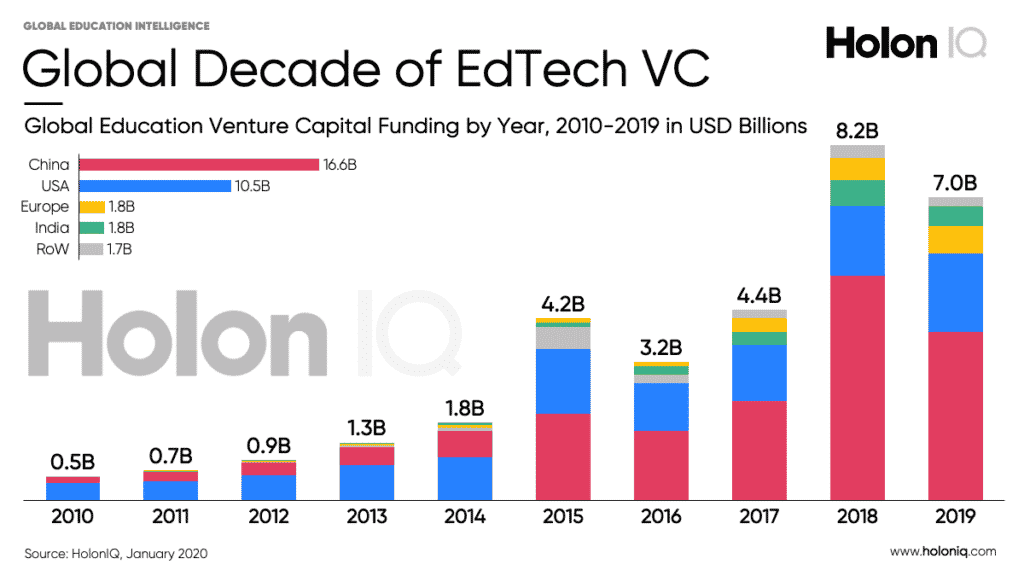
Driven by a number of macroeconomic factors (world population increase, better access to education in lower income countries), EdTech growth is primarily driven by the growth of Education expenditure itself.
Education expenditure is expected to grow to $10 Trillion by 2030, up 100% from its level today!
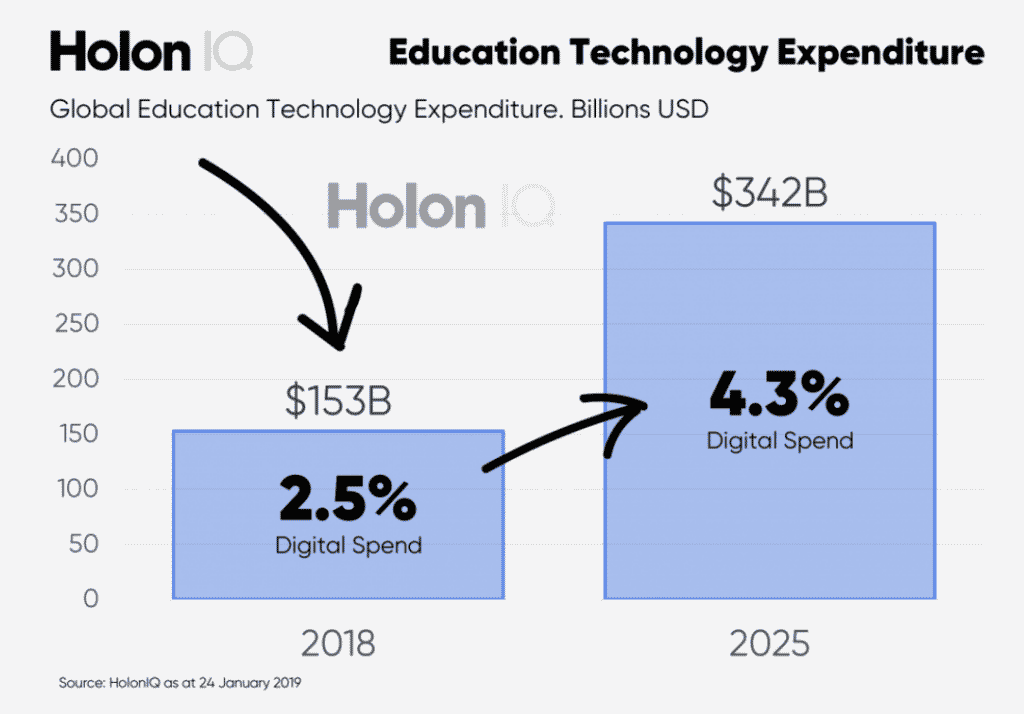
Of course, adoption of technology is a strong driver fuelling EdTech growth. It is estimated that technology only represents 3% of total education spend globally ($153 billion). This figure is expected to be 4.3% by 2025 ($342 billion).
What are the key trends driving EdTech?
There are a number of trends underlying EdTech growth and which are creating a number of opportunities for startups.
1. Online learning has gone mainstream
This is probably the obvious one: online learning has undeniably been fuelled by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Whilst online learning is more than 10 years old, Covid-19 has forced governments worldwide to adopt online learning processes within a few weeks in 2020.
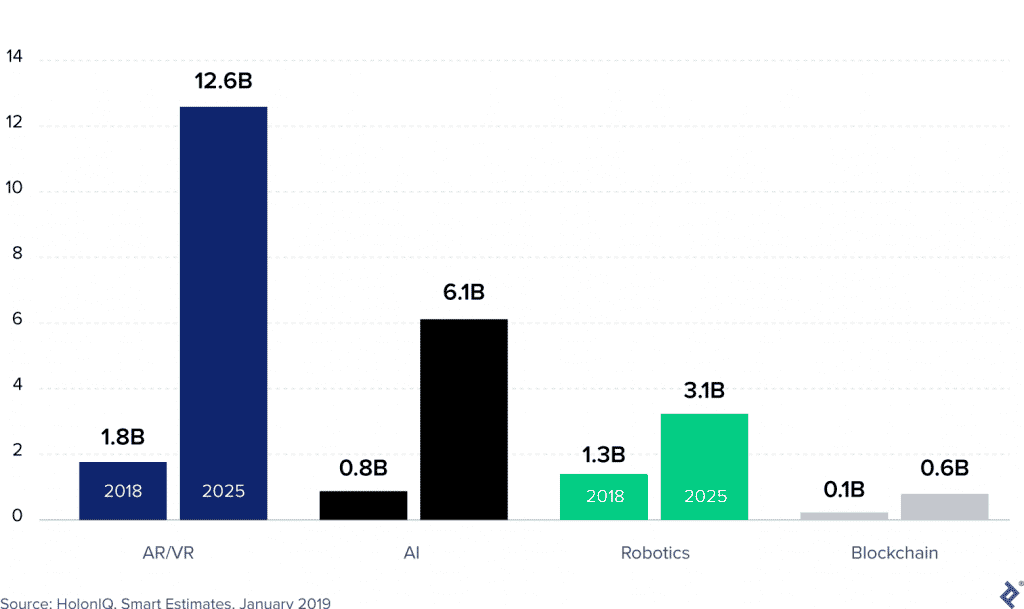
2. Emerging technologies to shape EdTech
New immersive technologies are gaining investor interest. A few examples are:
- Virtual reality (AR): Labster, Interplay Learning, etc.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning (adaptive learning): Quizlet, Kidaptive, etc.
- Robotics: Roybi for example uses robots and AI to help with early-stage learning and language acquisition
- Blockchain: obvious applications include verified degrees and credentials (Credly and Learning Machine are great examples of startups revolutionising EdTech through blockchain)
The 14 slides you need for your EdTech pitch deck
Every business is unique. Yet, venture capital firms and investors alike all agree on a common structure which we have laid out below.
Your EdTech pitch deck will likely be slightly different depending on whether you are pre-seed, seed or Series A+. Indeed, if you are pre-revenue for instance, you might not have early traction at all.
As rule of thumb, the more advanced your startup is the more content you should have in your pitch deck. Beware of endless, repetitive presentations: have clear titles, separate slides for each different topic.
Slide 1: Title
The title slide is the front page of your presentation.
Make sure your product or value proposition is clear from the outset: use an image of your product or, better, of your end-user application or instance (a consumer using your product).
Slide 2: The Problem
The problem slide is the “why” of your business. List here the 2/3 friction points you aim to fix with your product.
For example, online learning startups aim to fix the issue of accessibility, both geographically (you don’t need to travel or commute anymore to your class) and economically (online classes are more affordable as they require less investment for the same course quality).
Slide 3: The Solution
Your startup builds and commercialises a product and/or a service which solves the problem laid out on slide 2. The solution slide should not explain in detail your product nor how it works. Instead, focus on the benefits for your customers.
Ideally, you should compare the pain points explained on slide 2 (the problem) to the benefits your solution brings to your customers. That way, it is crystal clear to investors your solution really adds value to potential customers.
Following our online learning example above, 2 benefits could be:
- Affordable: learn the basics of web developments for $19.95 only with 50+ hours of online classes and exercise (e.g. Udemy for example)
- Convenient: no need to travel or commute to your class. Open your laptop and learn at any time of the day, whenever you want.
Slide 4: Market Opportunity
In the market slide, you need to clearly identify 2 very important metrics:
- Market size: how big is your market?
- Market growth: how fast does your market grow?
If you are operating in a niche market, chances are that you will face some challenges: the information might not be publicly available. In any case, you should be able to make a high-level estimation of your market. Read our article on market sizing and how to estimate TAM, SAM and SOM for your startup.
When looking for these metrics, you have multiple sources of information: public reports, specialised press, etc. Even public companies publish press releases and annual reports including some of their proprietary market estimates so be sure to look there too.
For important data points on the EdTech industry, have a look at our introduction at the beginning of this article.
Slide 5: Competition
The competition slide follows the market overview and must answer 2 key questions:
How fragmented is your market?
Are there 3 big players sharing 90% market share or thousands of small players? Here, refer to public market reports and your own understanding of the competitive landscape.
A few questions you could ask yourself, among others:
- Who are your competitors?
- Are they local, regional, national or global?
- Are there any product alternatives to your product?
- What about their IP / technological advantage?
Where do you position yourself vs. competition?
Is your solution a game changer other competitors don’t have (yet)? Do you have competitors with similar products/services?
Ideally, you would create a small table with, for each type of competitors and their main characteristics.
For instance, do they all a global presence? Do they cover all the products you offer? What is their relative price positioning (expensive vs. accessible)?
Slide 6: Revenue model
The revenue slide of your EdTech pitch deck is very important. Now that we have clearly identified the problem you are solving and the benefits of your solution, let’s have a closer look at how you generate revenue.
EdTech industries are very diverse, hence the scope of business models are very different from B2C to B2B startups.
Are you offering a subscription or a transaction revenue model? Also, explain clearly what is your pricing strategy: do you take a commission on property purchases? Do you charge interest on mortgage-related insurance products? etc.
Slide 7: Product
Here we need to explain clearly how your product works from a technological point-of-view. Include in your EdTech pitch deck product slide things such as:
- whether you have a white-labelled solution or a proprietary back-end / database
- what’s your intellectual property?
- how many full time front/back-end engineers you have
- how much you invested already in your tech
- Etc.
Slide 8: Go-to-market
The go-to-market slide of your EdTech pitch deck explains how you acquire your customers. Acquisition can either be online or offline (or both):
- Online acquisition: pay-per-click campaigns (e.g. Google Ads), content & SEO, social media, etc.
- Offline acquisition: print ads, events & fairs, mail, etc.
Arguably, most EdTech startups mostly use an online acquisition (especially for B2C EdTech businesses).
Online acquisition is sub-divided into 2 main categories itself:
- Inbound acquisition: customers convert from leads, at the top of funnel, who visit your landing page or website. These visitors (also referred to as “traffic”) either come from paid ads or organic sources (SEO, content)
- Outbound acquisition: customers are acquired via a sales team who actively reach out to potential customers. Because leads do not come by themselves but you reach out to them, this is an “outbound” strategy instead. Outbound is, for example, used by many B2B businesses (Enterprise SaaS for instance)
Note: to forecast customer acquisition, have a read at our article here (+ free template)
Slide 9: Traction
Only include the traction slide if you already have some early traction. Traction can be revenues for instance, but not necessarily (e.g. if you have sign-ups, free users, etc.).
As rule of thumb, the more historical performance you have, the more details you should give. For instance, if you start generating revenues 12 months ago and experienced a steady growth until then, include a bar chart of your revenues (or customers, patients, etc.) over the past 12 months.
Instead, if you have limited financial performance and/or numbers have been quite volatile, include today’s numbers instead.
Slide 10: Team
The team slide is one of the most important: investors invest in great teams before anything else.
The slide can either include the co-founding team only, but can also include key professionals and/or advisors as well.
Include key team members if they add real value.
Also, only include advisors if they are relevant to your industry. Do you have angel investors with significant experience who advise you on strategy? For instance, a PhD who acts as advisor to your EdTech startup (on regulation and market access matters for instance)?
For the team members’ details, keep it simple: name, position, years of experience and/or previous companies is more than enough.
Note: add a clickable link to the respective Linkedin profiles so investors can refer to a more exhaustive resume for your team members (if relevant)
Slide 11: Roadmap
The roadmap slide tells investors where you are going and how is product going to evolve in the future. You can either keep it high-level (e.g. your long-term strategy) or more detailed (e.g. the pipeline of the near-future product features).
Investors do not just invest in your product as it is today. For example, you might only have developed a MVP with limited features for early-adopters while your product could be tweaked and serve a much larger customer base in the future.
Also, you might be broadening the type of products you offer in the future. Or you might introduce premium services such as a subscription, or premium listing fees. All of these additional features are very important to add in your investment deck.
Slide 12: Financial Plan
Along with your product and the team, the financial plan slide is highly important. Unfortunately, many startups overlook the importance of financial projections in their EdTech pitch deck.
Think about your audience: investors (venture capital firms or angel investors) are financially literate individuals. As such, they invest in your business to generate returns. Logically, they care a lot about your financials and more especially, the expected financial performance of your business.
Do not expect investors to make up their own plan for your startup if you haven’t. As CEO, founder or entrepreneur alike, you should have a clear idea of where you are going.
As rule of thumb, the more advanced your startup is, the more granularity you should include here. Pre-seed startups might keep it short (1 slide) yet we recommend seed and Series A+ startups to include 2 slides instead.
Note: when presenting your financials, we recommend for pre-seed startup to show 3 years. Instead, seed and Series A+ startups should include 5 years projections as investors will likely ask for it for their own return analyses purposes.
Slide 13: Funding Ask
All pitch decks have a clear goal: raising capital from investors. The funding ask slide is where you clearly state your ask: how much are you raising?
Read our article on how to determine how much you should raise for you startup. While raising too little creates obvious problems, raising too much isn’t necessarily better.
On top of the amount, a good practice is to include a pie chart of where you will spend that money over a given period (your runway). Will you spend the bulk of it in product development to build your MVP? Or will you use a large portion in sales & marketing to commercialise your product and find product-market fit?
Our financial model templates include a cash burn dashboard where you can easily assess how much you should raise, and where you will spend your money. We also included charts ready to be included in your pitch deck. See how to use our cash burn dashboard here.
Slide 14: Contact
The contact slide is the last slide of your presentation. It has 2 main goals, this is where:
- You open the floor to questions from your audience when you are pitching
- You provide contacts (email and telephone) for investors who would only receive the PDF version of your presentation
- You open the floor to questions from your audience when you are pitching
- You provide contacts (email and telephone) for investors who would only receive the PDF version of your presentation

 5-year pro forma financial model
5-year pro forma financial model 20+ charts and business valuation
20+ charts and business valuation  Free support
Free support