General Practice Business Plan Template & PDF Example

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful general practice. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your general practice’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a general practice business plan, but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the healthcare industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your general practice concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
The Plan
Our general practice business plan is designed to encapsulate all fundamental components essential for a robust strategic framework. It details the clinic’s healthcare services, marketing plans, market conditions, competitive analysis, organizational hierarchy, and financial projections.
Here are the primary sections of our General Practice Business Plan:
- Executive Summary: Offers an overview of your General Practice’s business concept, market analysis, management team, and financial strategy.
- Business Overview: Provides detailed information on what your General Practice offers and its operational model:
- Practice & Location: Describes the practice’s facility, amenities, medical equipment, and the strategic significance of its location for patient accessibility.
- Services & Pricing: Lists the healthcare services your practice will provide, such as routine check-ups, preventive care, and chronic disease management, along with a pricing structure or insurance affiliations.
- Market Overview: Examines the healthcare industry landscape, identifying competitors and how your General Practice stands out:
- Key Stats: Shares relevant statistics about the general healthcare market, such as potential patient demographics, community health profiles, and healthcare spending trends.
- Key Trends: Highlights significant trends in healthcare that impact General Practices, like technological advancements in patient care, regulatory changes, and patient preference shifts.
- Key Competitors: Analyzes the main healthcare providers in the vicinity and differentiates your practice from them based on services, patient care quality, and operational efficiency.
- Strategy: Outlines how the General Practice intends to achieve growth and attract patients:
- SWOT: Conducts a Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats analysis to understand the internal and external factors influencing the practice.
- Marketing Plan: Describes strategies for patient acquisition and retention, including digital marketing, community outreach, and patient referral programs.
- Timeline: Sets key milestones and objectives from the practice’s establishment through the first year of operation, including critical stages like licensing, staff hiring, and service launch.
- Management: Provides information about the individuals managing the General Practice, detailing the backgrounds, roles, and expertise of the lead physicians and administrative team.
- Financial Plan: Projects the practice’s 5-year financial outlook, covering revenue streams, cost structure, profitability forecasts, and funding requirements.

Executive Summary
The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your General Practice’s business plan, providing a succinct outline of your medical practice and the healthcare services it offers. It will highlight your practice’s market positioning, detailing the comprehensive range of general healthcare services provided, its location, size, and a snapshot of daily operations.
This section will also delve into how your General Practice will assimilate into the local healthcare market, including an analysis of direct competitors in the vicinity, identifying who they are, and pinpointing your practice’s distinctive selling points that set it apart from these competitors.
Moreover, it’s important to include insights about the management and founding team, elaborating on their roles and how they contribute to the practice’s success. Additionally, a synopsis of your financial forecasts, encompassing revenue and profit expectations over the next five years, should be included to offer a clear view of your practice’s financial strategy.
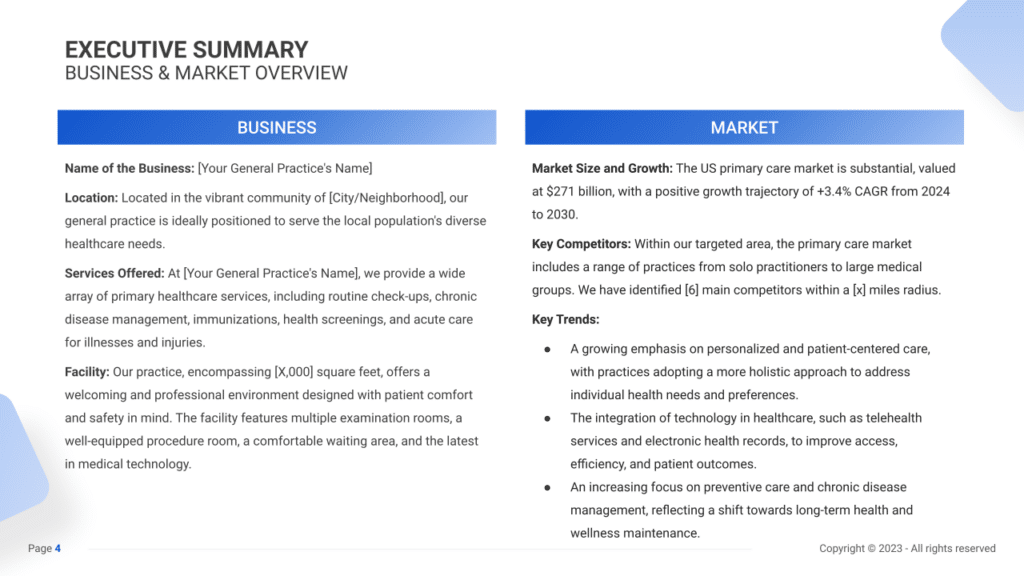
General Practice Business Plan Executive Summary Example

Business Overview
The business overview serves as the introductory platform for your general practice clinic. It should include essential information such as the clinic’s name, location, and an outline of its daily operations.
These details lay the foundation for showcasing the clinic’s unique qualities. Your clinic’s unique selling proposition (USP) is vital here, setting it apart in a competitive landscape. Whether it’s your focus on personalized patient care, innovative healthcare techniques, or community engagement, your USP should be a focal point of the executive summary. It highlights your clinic’s distinct value to its patients and the community.
Example:
“[Your General Practice’s Name],” strategically located in the heart of [City/Neighborhood], serves as a pivotal player in the expansive US primary care market valued at a substantial $271 billion. Our clinic, spanning [X,000] square feet, is meticulously designed to prioritize patient comfort and safety while offering a comprehensive suite of primary healthcare services. These services encompass routine check-ups, chronic disease management, immunizations, health screenings, and expedited care for various illnesses and injuries.
Market Overview
Understanding and conveying your general practice clinic’s target market is paramount. Detail the demographics, healthcare requisites, and industry trends to contextualize your clinic’s role and relevance within this landscape.
Equally imperative is the competitive landscape within the primary care domain. The market encompasses various healthcare entities, from independent practitioners to multi-specialty clinics and large healthcare networks. Understanding your competitors and articulating your clinic’s distinct value proposition is crucial. Whether your clinic specializes in comprehensive care, pioneering medical technology integration, or personalized patient experiences, showcasing these unique attributes sets the stage for your clinic to stand out and thrive amid competition.
Example:
The US primary care market presents significant opportunities, exhibiting a positive growth trajectory with a +3.4% CAGR from 2024 to 2030. Within our targeted area, the primary care landscape encompasses a variety of practices, including solo practitioners to large medical groups. We’ve identified [6] main competitors within a [x] mile radius, positioning ourselves to stand out within this competitive landscape.
Management Team
Highlight the expertise and qualifications of your management team, elucidating their proficiency in healthcare administration, operational management, and strategic planning.
Example:
Our leadership at [Your General Practice’s Name] comprises individuals with degrees in Healthcare Administration or Business Management, equipped with extensive experience in managing healthcare facilities. Their dedication to operational excellence and patient-centered care ensures the smooth functioning of our clinic, strategically positioning us within the competitive landscape.
Financial Plan
Concisely summarize your general practice clinic’s financial goals, emphasizing revenue targets, growth strategies, and investment plans.
Example:
With a strategic financial plan, [Your General Practice’s Name] aims to achieve $1.0 million in annual revenue and a 30% profit margin (EBITDA margin) by 2028. Our financial strategy involves prudent investments in advanced medical infrastructure, ongoing staff training, and targeted marketing initiatives. This positions our clinic for sustained growth and recognition within the community.
Business Overview
For a General Practice, the Business Overview section can be effectively organized into 2 main parts:
Practice & Location
Briefly describe the physical setup of your medical practice, focusing on how the space is designed for comfort and efficiency, ensuring a welcoming and professional atmosphere for patients. Mention the location of your practice, emphasizing how easy it is for patients to get there, such as its closeness to community centers or the availability of parking. Explain why this location is particularly good for reaching your intended patient group.
Services & Pricing
Detail the variety of medical services your practice offers, ranging from routine health check-ups and vaccinations to more specialized care such as chronic disease management, pediatric care, or women’s health services. Discuss your pricing strategy, making sure it aligns with the quality of care you provide and is competitive within the local healthcare market. Highlight any special offerings, such as health plans, preventive care packages, or loyalty discounts, that add extra value for your patients, promoting ongoing engagement and patient loyalty.


Market Overview

Industry size & growth
In the Market Overview of your General Practice business plan, begin by exploring the size of the healthcare industry, particularly focusing on general medical services, and its growth potential. This analysis is crucial for understanding the broad scope of the healthcare market and pinpointing areas for potential expansion.
Key market trends
Next, delve into the current trends within the healthcare sector, such as the growing demand for holistic and preventive healthcare, the integration of technology in patient care (telehealth, electronic health records, etc.), and a heightened focus on patient-centered services. Highlight the increasing preference for practices that offer comprehensive care plans, the use of digital tools for better health management, and the importance of accessibility and convenience in healthcare services.
Competitive Landscape
A competitive analysis is not just a tool for gauging the position of your general practice in the market and its key competitors; it’s also a fundamental component of your business plan. This analysis helps in identifying your general practice’s unique selling points, essential for differentiating your business in a competitive market.
In addition, competitive analysis is integral in laying a solid foundation for your business plan. By examining various operational aspects of your competitors, you gain valuable information that ensures your business plan is robust, informed, and tailored to succeed in the current market environment.
Identifying Competitors in the General Practice Industry
Start by pinpointing direct and indirect competitors in your area. Direct competitors may include other local general practices or medical clinics providing similar services. Indirect competitors might encompass urgent care centers, specialized clinics, or even telehealth services offering alternative healthcare solutions.
Leverage online tools like Google Maps or healthcare directories to visualize competitor locations. Review platforms like Healthgrades or Yelp for patient reviews and ratings. Understanding why patients praise a competitor’s prompt service or compassionate care can highlight their strengths in the market.
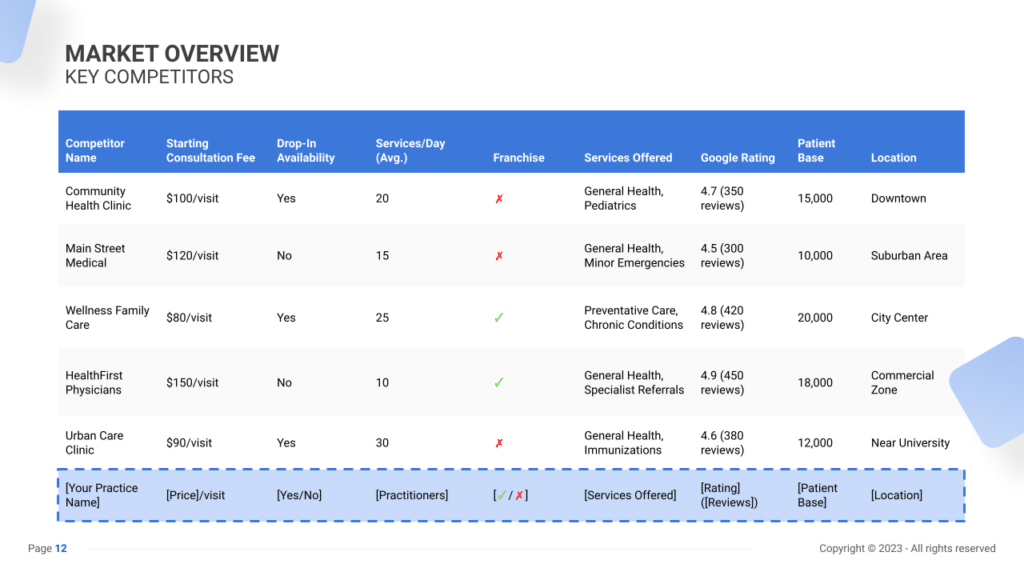
General Practice Competitors’ Strategies
Analyzing competitors’ strategies encompasses several facets:
- Service Offerings: Evaluate the range of services provided by competitors. For instance, if a nearby clinic excels in telemedicine services, it indicates a growing trend in remote healthcare accessibility.
- Medical Approach: Consider the medical philosophies or approaches adopted by competitors. A practice focusing on holistic wellness might attract a different patient demographic than one employing conventional medical treatments.
- Pricing and Insurance: Compare service fees and insurance acceptance. Are your rates competitive with those of nearby practices, or are you positioned as a premium service with additional amenities?
- Marketing and Patient Outreach: Analyze how competitors market their services. Do they leverage digital marketing, patient testimonials, or community engagement events for outreach?
- Patient Experience: Assess the overall patient experience. A clinic with a warm and welcoming environment might garner higher patient satisfaction compared to one with longer wait times or impersonal interactions.
- Technological Integration: Observe if competitors utilize innovative technologies like patient portals or AI-driven diagnostics to enhance healthcare delivery.
What’s Your General Practice’s Unique Value Proposition?
Reflect on what sets your practice apart. Maybe your clinic specializes in pediatric and geriatrics care or offers a comprehensive wellness program tailored for busy professionals.
Identify market gaps through patient feedback and industry trends. For instance, a growing demand for preventive healthcare services might present an opportunity to introduce wellness workshops or health coaching.
Consider location nuances: A practice in a bustling urban area might focus on convenience and swift appointments, while a suburban practice could emphasize a family-oriented approach with extended hours for working parents.
Strategy

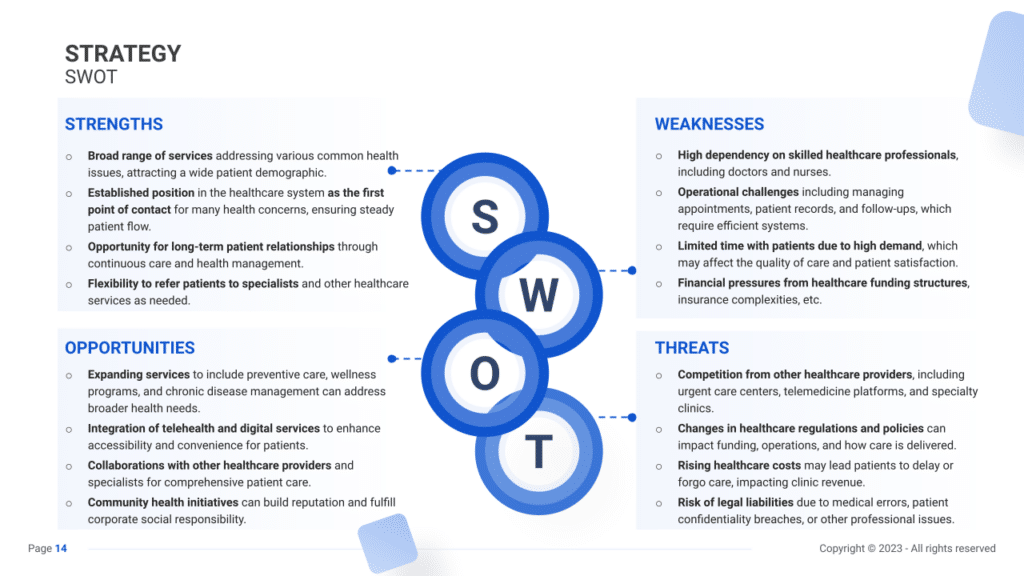
SWOT
First, carry out a SWOT analysis for your General Practice, identifying Strengths (such as experienced medical staff and comprehensive healthcare services), Weaknesses (like limited operating hours or high patient wait times), Opportunities (for instance, growing awareness and demand for preventive healthcare services), and Threats (such as changes in healthcare regulations or increased competition from other medical practices).
Marketing Plan
Then, devise a marketing strategy that details how to draw in and keep patients through focused advertising, health awareness campaigns, an active online presence, and participation in community health events.
Marketing Channels
Leveraging diverse marketing channels is essential to building brand visibility and engaging with patients effectively.
Digital Marketing
- Website and SEO: Your practice’s website is its digital storefront. Create an informative and user-friendly website highlighting services offered, patient testimonials, and healthcare insights. Optimizing the site for local SEO ensures higher visibility in search engine results.
- Social Media: Utilize platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn to share informative content, health tips, success stories, and updates. Engage with your audience through comments, direct messages, and live sessions to foster a sense of community and trust.
- Email Marketing: Build and maintain an email list offering healthcare tips, exclusive offers, and updates about new services or medical advancements.
Local Advertising and Community Engagement
- Community Events: Engaging with the local community through health fairs, wellness seminars, or free health screenings establishes your practice as an active participant in community well-being.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with local organizations, schools, or businesses to sponsor health-related events or educational sessions. Partnering with community leaders or influencers can amplify your practice’s reach within the local population.
Promotional Activities
- Special Deals: Offer seasonal health check-up packages or introductory discounts for new patients to encourage a trial of your services. Limited-time promotions can attract new patients and encourage existing ones to book additional appointments.
- Loyalty Programs: Implement a structured loyalty program where patients earn points for each visit or referral, redeemable for discounts on healthcare services or health-related products.
- Referral Programs: Incentivize existing patients to refer new patients by offering rewards such as discounted services, free consultations, or other value-added services.

Sales Channels
Deploying effective sales strategies ensures patient satisfaction and maximizes revenue opportunities.
In-Practice Upselling
- Additional Services: Train your staff to suggest additional preventive screenings, health assessments, or vaccinations during patient visits.
- Health Products: Display health-related products, supplements, or health aids within the practice.
- Service Packages: Offer bundled healthcare services or comprehensive health check-up packages at discounted rates. These packages encourage patients to avail themselves of a broader range of services.
Online Booking and Sales
- Online Appointment System: Implement an easy-to-use online appointment booking system through your website or dedicated mobile app. Offer incentives, such as a small discount or a complimentary service, for booking appointments online.
- E-commerce: Extend your services beyond the clinic by selling health-related products, supplements, or wellness kits directly through your website. This not only adds convenience for patients but also opens up an additional revenue stream for the practice.
- Telehealth Services: Provide teleconsultation services for patients seeking remote medical advice, follow-ups, or preliminary assessments. Offering telehealth services enhances accessibility for patients with time constraints or mobility issues.
Membership and Loyalty Programs
- Membership Benefits: Develop membership plans offering regular health check-ups, preventive care, or discounted rates for ongoing treatments for a fixed monthly or annual fee. These plans ensure consistent patient engagement and encourage regular healthcare check-ups.
- Loyalty Rewards: Establish a digital rewards system where patients earn points for each visit or referral, redeemable for free services, discounts on healthcare treatments, or exclusive offers. This fosters patient loyalty and satisfaction.
Strategy Timeline
Lastly, establish a detailed timeline that marks important steps for the General Practice’s launch, marketing activities, patient base development, and goals for growth, ensuring the practice progresses with a clear and deliberate strategy.

Management
The Management section focuses on the general practices’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the general practice toward its financial and operational goals.
For your general practice business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the business.


Financial Plan
The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of your financial projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out your general practice’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your general practice business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your key assumptions (e.g. number of customers and prices, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here
_ Profit and Loss
_ Cash Flow Statement
_ Balance Sheet
_ Use of Funds









