Medical Clinic Business Plan Template & PDF Example

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful medical clinic. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your medical clinic’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a medical clinic business plan but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the healthcare industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your medical clinic concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
The Plan
Our medical clinic business plan is carefully designed to cover all the important parts needed for a good strategy. It explains how the clinic will run, how we’ll take care of patients, how we’ll tell people about our services, what the healthcare situation is like, who our competitors are, who’s in charge, and how much money we expect to make.
- Executive Summary: Provides an overview of the Medical Clinic’s business concept, healthcare market analysis, management structure, and financial strategy.
- Business Overview: Detailed information on what the medical clinic offers and its operational model.
- Facility & Location: Describes the clinic’s physical setup, including its architectural design, medical equipment, patient amenities, and the strategic choice of its location to maximize accessibility for its target patient base.
- Treatments & Pricing: Enumerates the healthcare services the clinic will provide, from general medical consultations to specialized treatments, alongside a transparent pricing model.
- Market Overview: Examines the healthcare industry landscape, identifies competitors, and shows how the clinic stands out.
- Key Stats: Shares industry size, growth trends, and relevant statistics for the healthcare market.
- Key Trends: Highlights recent trends affecting the healthcare sector, such as technological advancements, patient care innovations, and regulatory changes.
- Key Competitors: Analyzes the main competitors in the vicinity and differentiates the clinic based on services, patient care quality, and operational efficiency.
- Strategy: Outlines how the medical clinic intends to achieve growth and attract patients.
- SWOT: Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats analysis tailored to the healthcare context.
- Marketing Plan: Strategies for attracting and retaining patients, including digital marketing, community health programs, and patient service excellence.
- Timeline: Key milestones and objectives from the clinic’s establishment through the first year of operation, including licensing, staff recruitment, and service launch.
- Management: Information on the healthcare professionals managing the medical clinic and their roles, emphasizing their medical expertise and healthcare management experience.
- Financial Plan: Projects the clinic’s 5-year financial performance, including revenue from medical services, operational costs, profits, and expected expenses, ensuring a sustainable and profitable healthcare service model.

Executive Summary
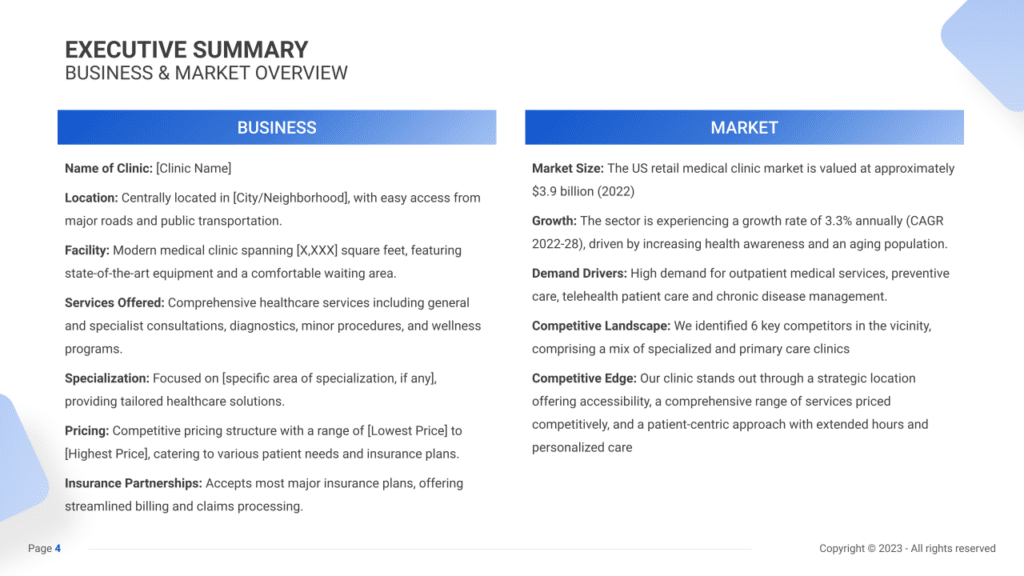
The Executive Summary introduces our medical clinic’s business plan, offering a concise overview of the clinic and its healthcare services. It details our market positioning, the comprehensive medical services we provide, its location, size, and an outline of our day-to-day operations.
This section will also delve into how our clinic will integrate into the local healthcare market, including an assessment of the direct competitors in the area, identifying who they are, and highlighting our clinic’s unique selling points that set us apart.
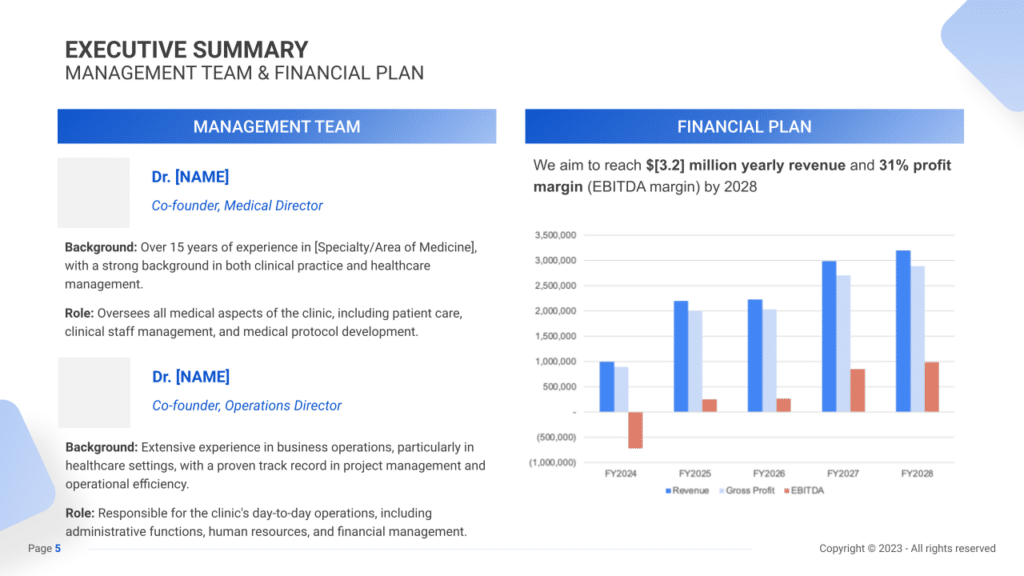
Additionally, it includes information about our management and co-founding team, outlining their roles and contributions to the clinic’s success. A summary of our financial projections, including expected revenue and profits over the next five years, will also be presented to offer a clear view of our clinic’s financial outlook.
Medical Clinic Business Plan Executive Summary Example
Business Overview
In the business overview, you should clearly define your gym’s characteristics. This includes its name, location, facility details, membership plans, and the variety of classes offered. This part of the summary is critical for showcasing what makes your gym stand out in a competitive fitness industry.
Example:
For instance, “FitFusion Gym,” situated in the city center, offers a 15,000 sq. ft. space with an open-plan design and state-of-the-art equipment. Its unique selling points include a comprehensive range of fitness classes, from HIIT to Yoga, and premium amenities like a wellness center. These features position FitFusion as a versatile and appealing fitness destination.
Market Overview
In this section, you should analyze the gym market, including its size, growth trends, and key competitors. This gives context to where your gym fits within the industry and highlights how it can capitalize on current fitness trends.
Example:
FitFusion Gym enters a robust U.S. market valued at $30.8 billion. It sets itself apart from the five main competitors in its vicinity by offering a blend of holistic wellness and cutting-edge fitness technology, tapping into the growing demand for integrated health and fitness experiences.
Management Team
Detailing the experience and roles of your management team is vital. This section should highlight their qualifications in gym and wellness management, underscoring their ability to drive the gym’s success.
Example:
The CEO of FitFusion brings extensive experience in fitness management, guiding the gym’s strategic direction and operations. The CFO & Marketing Director, with a strong background in finance and marketing, plays a crucial role in managing the gym’s finances and developing effective marketing strategies to enhance customer engagement and retention.
Financial Plan
A clear presentation of financial goals and projections is key in this section. It should include targets for revenue and profit margins, offering insight into the gym’s financial health and growth prospects.
Example:
With a target of $2.0 million in yearly revenue and a 22% profit margin by 2027, FitFusion Gym is positioned for significant growth. Its financial strategy is supported by an ambitious marketing approach and a focus on delivering exceptional customer experiences, aligning the gym for success in the competitive fitness market.
Business Overview
For a medical clinic, the Business Overview section can be concisely structured into 2 main components:
Facility & Location
Briefly describe the clinic’s facilities, highlighting the state-of-the-art medical equipment, patient-centric design, and a welcoming atmosphere that ensures comfort and privacy.
Mention the clinic’s strategic location, emphasizing its accessibility and conveniences such as proximity to main transit routes and ample parking. Explain how this location was selected to serve the clinic’s target patient demographics effectively.
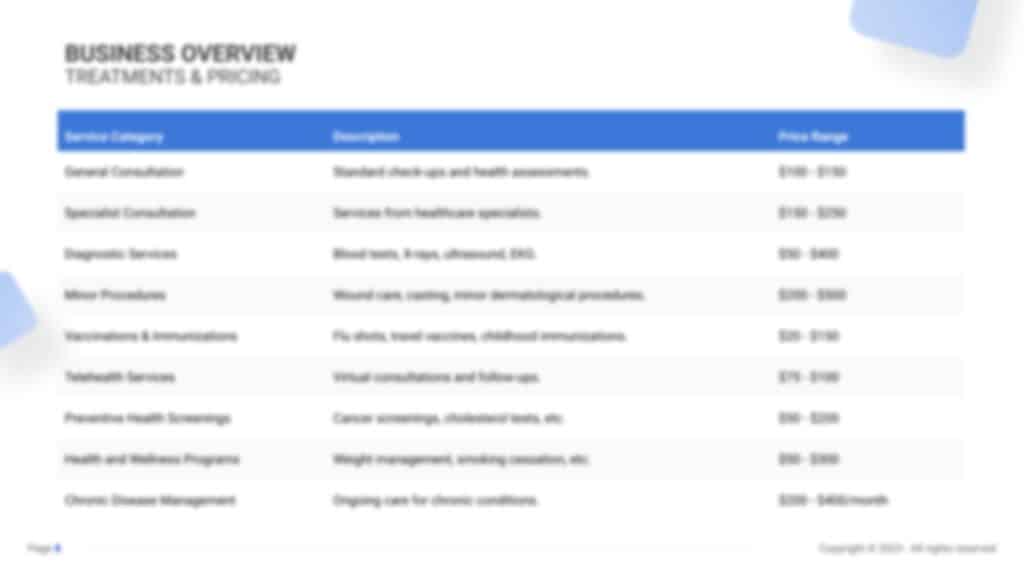
Treatments & Pricing
Detail the comprehensive range of medical services provided, from routine health check-ups to specialized treatments in areas like cardiology, pediatrics, or orthopedics.
Describe your pricing model, ensuring it mirrors the high standard of care offered and is competitive within the healthcare market. Highlight any health plans, membership options, or loyalty programs designed to offer added value to patients, fostering long-term relationships and patient loyalty.

Market Overview
Industry size & growth
Start your medical clinic business plan by looking at how big the healthcare world is, especially for the services you provide like general health, special treatments (skincare, children’s health), or quick care. Think about how this area is growing and where you might find new chances to grow.
Key market trends
Then, talk about what’s new in healthcare, like how people want care that’s just for them, using tech to help patients (like video doctor visits or digital health records), and focusing on keeping people healthy before they get sick. Point out that people are looking for services that meet their specific health needs and that there’s a growing interest in clinics that care for the whole person.
Competitive Landscape
A competitive analysis is not just a tool for gauging the position of your medical clinic in the market; it’s also a fundamental component of your business plan.
This analysis helps in identifying your medical clinic’s unique selling points, essential for differentiating your business in a competitive market.
In addition, competitive analysis is integral in laying a solid foundation for your business plan. By examining various operational aspects of your competitors, you gain valuable information that ensures your business plan is robust, informed, and tailored to succeed in the current market environment.
Identifying Competitors in the Healthcare Sector
Begin by mapping out direct and indirect competitors in the healthcare industry. Direct competitors might include other medical clinics, specialized treatment centers, or hospitals offering similar services within your local area.
Additionally, consider indirect competitors such as urgent care facilities, telemedicine services, or alternative medicine practitioners that might attract your target patients.
Utilize online tools and directories, such as Google Maps and healthcare-specific platforms like Healthgrades or Zocdoc, to gain insights into the distribution and offerings of competitors.
Patient reviews and ratings on these platforms offer valuable information about competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. For instance, glowing reviews highlighting short waiting times and personalized care at a rival clinic indicate a competitive advantage worth noting.

Medical Clinic’s Competitors’ Strategies
Analyzing competitors’ strategies involves evaluating several facets:
- Services Offered: Assess the range of medical services and specialties offered by competitors. For instance, if a neighboring clinic specializes in integrative medicine or offers holistic approaches, it may attract a different patient demographic than a clinic focusing solely on traditional treatments.
- Treatment Approaches: Consider the medical philosophies and approaches adopted by rival clinics. A clinic known for evidence-based treatments may appeal to a different patient base than one embracing alternative therapies or holistic healing methods.
- Pricing and Payment Models: Compare pricing structures and payment models offered by competitors. Determine if your clinic’s pricing aligns with those of budget-friendly clinics or premium healthcare service providers in your area.
- Marketing and Patient Outreach: Analyze competitors’ marketing strategies. Do they heavily invest in digital marketing, have a strong online presence, or engage in community health programs and events?
- Patient Experience: Evaluate the patient experience at rival clinics. For instance, a competitor might be recognized for its friendly staff, minimal waiting times, or advanced appointment scheduling systems, contributing to an enhanced patient experience.
- Operational Efficiency and Technology Integration: Observe if competitors leverage technology to streamline patient management and appointment scheduling or offer telemedicine services for remote consultations.
What’s Your Clinic’s Value Proposition?
Reflect on your clinic’s unique value proposition. This could include specialized treatments, cutting-edge medical technology, a focus on personalized patient care, or convenient access to healthcare services.
Identify gaps in the market through patient feedback and healthcare trends. For example, if there’s an increasing demand for preventive care or a specific medical service in your area that competitors aren’t adequately addressing, this presents an opportunity for your clinic.
Consider your clinic’s location and community demographics. Tailor your services to meet the needs of the local population-urban clinics might emphasize convenience and efficiency, while clinics in residential areas could focus on building stronger patient relationships and community engagement.
Strategy
SWOT
First, conduct a SWOT analysis for the medical clinic, identifying Strengths such as a team of expert medical professionals and a comprehensive suite of healthcare services. Weaknesses might include factors like high operational costs and the complexity of insurance processes. Opportunities can arise from the growing emphasis on health and wellness and the potential for telemedicine services. Threats could stem from increased competition and the impact of economic downturns on discretionary healthcare spending.

Marketing Plan
Next, develop a marketing strategy aimed at attracting and retaining patients. This strategy should focus on targeted advertising to reach specific demographics, offering promotional incentives for referrals, maintaining an active and engaging presence on social media, and fostering community ties through health education and events.
Marketing Channels
Deploy a diverse array of marketing channels to effectively reach potential patients and cultivate lasting relationships.
Digital Marketing
- Website and SEO: Develop a comprehensive website housing detailed information about your services, healthcare professionals, patient testimonials, and educational resources. Optimize it for local SEO to enhance visibility and attract local patient traffic.
- Social Media: Utilize various social media platforms – LinkedIn for professional networking and educational content, Facebook for community engagement and healthcare updates, and Instagram for visual storytelling and patient education.
- Content Marketing: Regularly publish informative blog posts, articles, and videos addressing prevalent health concerns, treatment options, preventive care measures, and breakthroughs in the medical field. This content serves to establish your clinic’s expertise and attract patients seeking credible information.
Local Advertising
- Community Engagement: Sponsor or participate in local health fairs, wellness events, or educational seminars aimed at fostering health awareness within the community. These events offer a platform to educate the public about prevalent health issues and position your clinic as a reliable source of healthcare information.
- Collaborations: Forge partnerships with local gyms, wellness centers, corporate offices, or community organizations to offer healthcare screenings, educational workshops, or health campaigns. Collaborative efforts broaden your reach and establish your clinic as an integral part of the community’s well-being.
Promotional Activities
Engage potential patients through compelling offers and initiatives:
- Free Consultations: Introduce a promotional campaign offering free initial consultations for new patients. This initiative provides an opportunity for patients to experience your clinic’s services and expertise firsthand.
- Referral Programs: Create a structured referral program incentivizing existing patients to refer others to your clinic. Offer discounts, loyalty points, or small rewards for successful referrals, fostering a sense of community and trust.
- Seasonal Health Campaigns: Launch health-related campaigns aligned with seasonal health concerns (e.g., flu vaccination drives and summer wellness check-ups) to draw attention to your clinic’s services and encourage visits during these periods.

Sales Channels
Efficient sales channels are vital for patient engagement and service delivery optimization.
Appointment Optimization
- Online Booking: Implement a user-friendly online appointment scheduling system accessible through your website and social media channels. Simplifying the booking process enhances patient convenience and accessibility to your services.
- Telemedicine Services: Introduce telemedicine services for non-emergency cases, providing patients with remote access to healthcare consultations and follow-ups. Telehealth services cater to the evolving needs of patients seeking convenient healthcare solutions.
Patient Retention Strategies
- Patient Experience Enhancement: Focus on providing exceptional patient care, personalized attention, and consistent follow-up communication. Creating a positive patient experience fosters patient loyalty and encourages referrals, augmenting your clinic’s reputation.
- Membership Programs: Develop membership plans offering regular check-ups, discounts on services, or additional perks for loyal patients. Membership programs instill a sense of exclusivity and reward patient loyalty, leading to increased patient retention rates.
Strategy Timeline
Finally, create a detailed timeline that marks essential milestones for the clinic. This includes the initial setup and opening phase, followed by the launch of marketing initiatives, efforts to expand the patient base, and strategies for broader service offerings, all designed to ensure the clinic progresses with a clear and defined purpose.

Management
The management section focuses on the medical clinic’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the medical clinic toward its financial and operational goals.
For your medical clinic business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the medical clinic’s mission.

Financial Plan
The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of the medical clinic’s financial strategy, including projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out the clinic’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your medical clinic business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your main assumptions (e.g. prices, customers, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here
_ Profit and Loss
_ Cash Flow Statement
_ Balance Sheet
_ Use of Funds