Little Caesars Franchise FDD, Profits & Costs (2025)

Little Caesars, a leading pizza franchise, was founded in 1959 by Mike and Marian Ilitch in Garden City, Michigan. It began franchising in 1962 and is now the third-largest pizza chain globally, with headquarters in Detroit.
The brand is known for its “Hot-N-Ready” model, launched in 2005, offering ready-made pizzas without the need for advance orders. This feature has fueled its success.
Along with pizzas, Little Caesars offers a range of side dishes, making it a go-to for quick, affordable meals. The franchise is expanding aggressively, targeting new markets with multi-unit franchises and locations like convenience stores and college campuses. Its simple model and brand recognition make it a top choice for entrepreneurs.
Little Caesars Franchise Initial Investment
How much does it cost to start a Little Caesars franchise? It costs on average between $447,000 – $1,817,000 to start a Little Caesars franchised restaurant.
This includes costs for construction, equipment, inventory, and initial operating expenses. The exact amount depends on various factors, including the type of restaurant you choose, the location, and whether the franchisee chooses to lease or purchase the property.
| Type of Expenditure | Amount |
|---|---|
| Initial Franchise Fee | $20,000 |
| Rent | $1,500 – $7,000 |
| Leasehold Improvements | $50,000 – $1,000,000 |
| Supplies and Equipment from Blue Line | $250,500 – $369,500 |
| Other Fixtures, Equipment, and Signage | $15,000 – $158,000 |
| Grand Opening Advertising | $15,000 |
| Training Expenses | $12,000 – $16,500 |
| Start-up Inventory and Supplies | $63,000 – $154,000 |
| Insurance | $500 – $1,200 |
| Utility Expenses | $1,000 – $9,000 |
| Licenses and Permits | $1,000 – $20,000 |
| Additional Funds – 3 Months | $17,000 – $47,000 |
| Total | $446,500 – $1,817,200 |
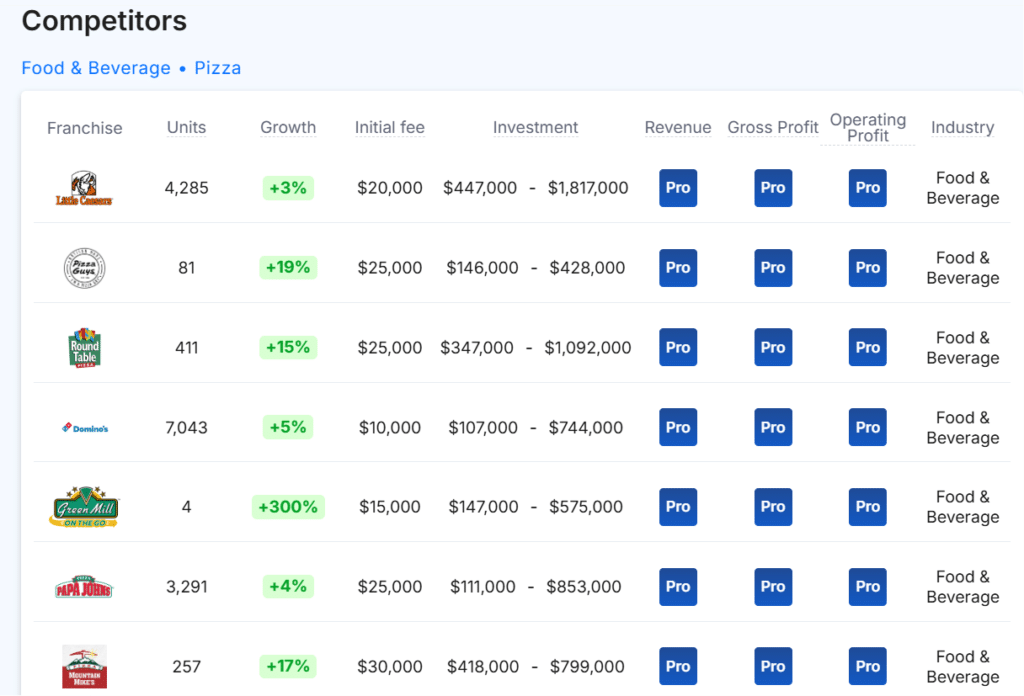
Competitors
Below are a few Little Caesars competitors as a comparison:
Download the Franchise Disclosure Document
Frequently Asked Questions
How many Little Caesars locations are there?
As of the latest data, Little Caesars has approximately 4,285 locations in the United States. Of these, the majority are franchise-owned, with around 3,785 franchised outlets. The remaining locations, around 580, are company-owned.
What is the total investment required to open a Little Caesars franchise?
The total investment required to open a Little Caesars franchise ranges from $447,000 – $1,817,000 for a single Little Restaurant.
What are the ongoing fees for a Little Caesars franchise?
For a Little Caesars franchise, the royalty fee is the greater of 6% of gross sales or a minimum of $300 per week. This fee is paid weekly and helps cover the franchise’s operational support and access to the brand’s systems. Additionally, franchisees are required to pay an advertising fee of up to 7% of gross sales.
This fee supports national and local marketing efforts, ensuring that the brand remains visible and competitive in the market.
What are the financial requirements to become a Little Caesars franchisee?
To become a Little Caesars franchisee, prospective franchisees must have a minimum net worth of at least $350,000.
Additionally, they are required to have a minimum of $150,000 in liquid assets. These financial thresholds ensure that franchisees have the necessary resources to cover initial startup costs and maintain financial stability during the operation.
Who owns Little Caesars?
Little Caesars is owned by the Ilitch family. The pizza chain was founded in 1959 by Mike Ilitch and his wife Marian Ilitch in Garden City, Michigan.
It remains a family-owned business under the Ilitch Holdings umbrella, which also controls several other ventures, including the Detroit Tigers (MLB) and the Detroit Red Wings (NHL). After Mike Ilitch’s passing in 2017, Marian Ilitch continued overseeing the family’s business interests.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: This content has been made for informational and educational purposes only. We do not make any representation or warranties with respect to the accuracy, applicability, fitness, or completeness of the information presented in the article. You should not construe any such information or other material as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other professional advice. Nothing contained in this article constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, advertisement, or offer to buy or sell any franchises, securities, or other financial instruments in this or in any other jurisdiction in which such solicitation or offer would be unlawful under the franchise and/or securities laws of such jurisdiction.
All content in this article is information of a general nature and does not address the detailed circumstances of any particular individual or entity. Nothing in the article constitutes professional and/or financial and/or legal advice, nor does any information in the article constitute a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. You alone assume the sole responsibility of evaluating the merits and risks associated with the use of any information or other content in this article before making any decisions based on such information or other content.




