How Profitable is a Pizzeria? Profits & Breakeven Analysis

If you are planning to open a pizzeria, you may want to know how much profits you can make with this business. In other words, you must know how much revenue you must generate to reach break-even and make profits.
With a market size of about $46 billion and over 75,000 pizzerias in the US, the average pizza shop has an annual turnover of $600,000..!
What does this mean for your pizzeria? How much revenues can you expect to generate? More importantly: how much profits can you realistically make with a pizzeria?
In this article we’ll look into the average revenues and profit margins of a pizzeria in the US. We’ll also look into how you can accurately forecast your pizzeria’s turnover and break-even point. Let’s dive in!
What is the average turnover for a pizzeria?
As per Statista, With a market size of about $46 billion and over 75,000 pizzerias in the US, the average pizza shop has an annual turnover of $600,000.
However, remember that it is only an average value and includes big franchises like Domino’s, Papa John’s, and Little Caesars, etc. These franchises actually account for the lion’s share of the total annual revenue.
When it comes to pizza shops owners’ salaries, PayScale says that the national average salary is $60,000 in the US.
What is the average profit margin for a pizzeria?
According to BNG Payments, the average profit margin for pizza businesses is about 15%.
These are industry averages though, and vary a lot from one pizzeria to another. In our experience, profits can be estimated by preparing financial projections.
Indeed, profits for a pizzeria vary based on 2 factors: your revenues and expenses.
We already saw how much turnover earns the average pizzeria in the US (~$600,000), let’s now see how much it costs to run a pizza shop.
How much does it cost to run a pizzeria?
Operating a pizzeria attracts some costs that include:
- COGS: You need to spend money on acquiring the raw materials (or inventory) required for your business operations
- Salaries: You need to pay salaries to your employees
- Rent & utility bills: Unless you own the commercial space where you are running your pizzeria, you must pay rent. Even if you own the space, you will most likely need to pay monthly mortgage installments. Plus, you need to pay off the utility bills you receive each month
- Marketing: Unless you advertise and market your pizzeria properly, you will not receive enough customers, and hence, you need to have a monthly marketing budget
- Insurance: You will require business insurance, workers’ compensation insurance, and several other types of insurance for which you must pay a monthly installment
- Software: You will require a variety of software such as POS software, bookkeeping software, etc. to run your business efficiently. Usually, they have monthly charges
- Miscellaneous: You will need to pay for cleaning and janitorial services
In general, it costs between $33,000 and $41,000 per month to run a small pizzeria that makes $35,000 – $45,000 in sales per month. For more information on how much it costs to run a pizzeria, read our article here.
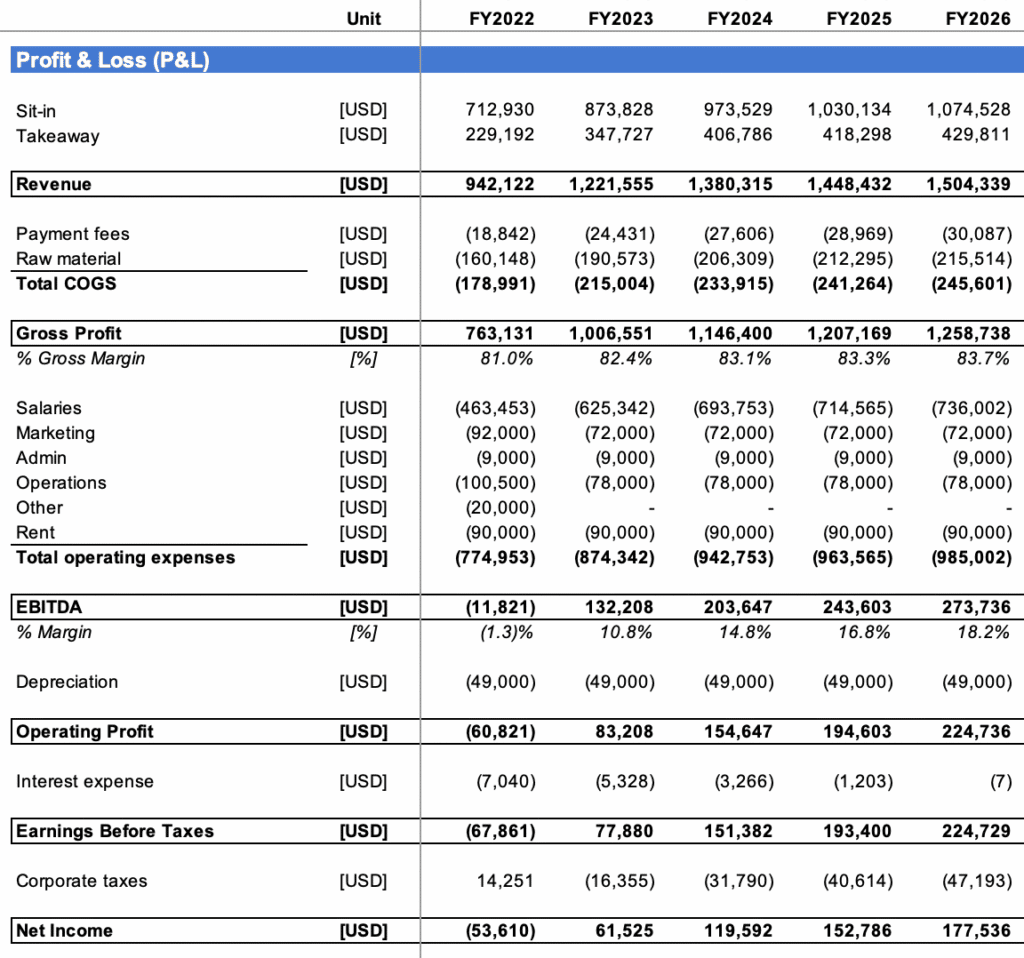
For clarity, we have included below the turnover to net profit waterfall for an illustrative pizza shop in the US operating both takeaway and a sit-in pizza restaurant ($1,200,000 revenue per year and ~4% net profit margin). By far the largest expenses are salaries (~50% total revenues).
How to forecast profits for a pizzeria?
In order to calculate profits for a pizzeria, you must first forecast revenues and expenses.
Profits = Revenue – Expenses
Forecasting revenue for a pizzeria
Revenue can easily be obtained by multiplying the number of orders by the average order value:
Revenue = Orders x Average order value
For example, if you have 100 orders in a day with an average order value of $20, monthly revenue is about $50,000 (assuming 6 days a week).
Forecasting expenses for a pizzeria
There are 2 types of expenses for a pizzeria:
- Variable expenses: these are the COGS as explained earlier. They grow in line with your revenue: if your turnover increases by 10%, variable expenses grow by 10% as well
- Fixed expenses: salaries, rent, debt interest (or leasing) costs to acquire the equipment, marketing and all the other operating costs listed above
Calculating profits for a pizzeria
When we refer to profits, we usually refer to EBITDA (Earnings before interests, taxes, depreciation and amortization) as it represents the core profitability of the business, excluding things such as debt interests, non cash expenses and other non-core expenses.
In order to get to EBITDA, we use the following formula:
EBITDA = Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses
Whilst gross margin stands at about ~83%, EBITDA margin can go up to 15-20% depending on the business and net profit margin up to 5-10% for the most profitable pizzerias (in line with the industry averages discussed above).
How to calculate break-even for a pizzeria?
Break-even is the point at which total costs and total revenue are equal. In other words, the breakeven point is the amount of revenue you must generate to turn a profit.
Because you must at least cover all fixed costs (that aren’t a function of revenue) to turn a profit, the break-even point is at least superior to the sum of your fixed costs.
Yet, you also need to spend a certain amount for every $1 of sales to pay for the variable costs.
As we just saw, pizza shops typically have a ~80% gross margin (after raw materials and payment fees). Indeed, most expenses actually are fixed costs (salaries, rent, marketing, etc.).

The break-even point can easily be obtained by using the following formula:
Break-even point = Fixed costs / Gross margin
Using the same example earlier, let’s assume your pizzeria makes $50,000 in turnover per month and has the following cost structure:
| Operating cost | Fixed vs. variable | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Raw materials | Variable cost | $9,000 |
| Staff costs | Fixed cost | $25,000 |
| Rent, bills | Fixed cost | $5,000 |
| Marketing | Fixed cost | $4,000 |
| Other | Fixed cost | $4,000 |
| Total | $47,000 |
The break-even point would then be:
Break-even point = Fixed costs / Gross margin %
= $38,000 / 80% = $47,500
In other words, you need to make at least $47,500 in sales per month to turn a profit.
Assuming the average order value is $20, your break-even is 2,375 orders per month. In other words, you make profits once you have at least 95 orders a day (assuming you’re open 6 days a week).
How to increase profits for a pizzeria?
There are several ways to increase profits for a pizzeria and they include:
- Professional Photography: Professional food photography helps to attract more customers. Hence, consider professional photography for your best-selling products
- Sell By Slice: Not everyone wants a full pizza. Selling slices can attract more customers
- Mobile Ordering: Introduce mobile ordering to increase order frequency and improve service speed. This in turn pleases customers and helps to increase the order value
- Control Specialty Ingredient Usage: If there are special ingredients that you use, make sure that you use them only for premium products and charge accordingly
- Provide Delivery: People prefer food to be delivered to their doorstep, and this is especially true after the COVID-19 pandemic. Introduce your own delivery system or partner with food delivery services
- Approach Schools, Colleges, and Offices: Contact these organizations and talk to them to allow you to sell pizza in their cafeteria
- Offer Coupon Discounts: Coupon discounts can increase the footfall to your pizzeria and hence, your profits
- Use Loyalty Programs: Loyalty programs are a great way to increase the lifetime value of customers. Happy customers also help with word-of-mouth advertisements and help to bring in more customers
- Upsell & Cross-sell: You must teach your staff to upsell and/or cross-sell to increase overall profits
- Reduce Waste: Use inventory management to reduce wastage, which in turn helps to increase profits
- Optimize Energy Efficiency: Reduce energy and fuel costs by regularly cleaning vents, exhaust hoods, drainage hoses, HVAC filters, etc. Also switch to LED lighting, keep oven doors closed, insulate the attic, and so on.