SBA Business Plan Template: Full Guide [2023]

In 2020, SBA’s flagship 7(a) loan program approved more than 42,000 loans totalling $22 billion. Yet, SBA loans are notoriously difficult to obtain for small businesses: less than 15% of SBA loan applications were granted by big banks. If you’re applying for a SBA loan, you will need a solid business plan template for your loan application.
In this article we go through, step-by-step, all the different sections you need in your business plan to build a complete, clear and solid business plan lenders will approve. Read on!
Why do you need a business plan for your SBA loan application?
Other than your basic eligibility requirements, the primary element that lenders would review is your business plan. Having a good business plan determines if your business is a lucrative opportunity for SBA lenders.
Also, a solid business plan makes it easier to get your loans approved because banks would be confident that your business would be successful and you would be able to repay your loan.
However, business plans tend to differ depending on the nature and status of your business. If you’re running an independent business or launching a startup for example, your business plan will be reviewed more thoroughly.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary is the most important page of your SBA business plan template. We can’t make this clearer. This is the first section that the lenders will have a look at.
Before we go into specifics, keep in mind the executive summary actually is a summary. Keep it brief: your executive summary should never be more than 2 pages maximum.
Your executive summary should consists of 5 parts:
- The “mission statement“: what problem(s) is your business solving?
- Product and service: what is it that you sell? to whom? where?
- People: who are the founders / management? What about their experience? How many people / teams do you employ?
- Key financials and projections: what are your key metrics and financials today (revenues, customers, etc.)? What do you expect these to be in 3/5 years from now?
- Funding ask: what (how much) are you asking as part of this loan? Where will you spend it? For what?
2. Company description
The company description is where we go into more details about your business, and which problem(s) it actually solves.
You should explain here clearly:
What is the problem at stake?
You should list here the 2/3 friction points you aim to tackle.
Remember: even if your business isn’t necessarily innovative, your business is potentially solving a problem, as obvious as it may be, for many people out there. The more obvious the problem is, the more people it affects, the better
What is your solution?
Your business is commercialising a product and/or a service which solves the problem mentioned above. Here, you should explain 2 things: how your product / service works, and what benefits it brings to your customers.
Ideally, you should compare the pain points explained earlier (the problem) to the benefits your solution brings to your customers. That way, it is crystal clear to lenders and investors your solution really adds value to potential customers.
When explaining your business’ solution, you should explain clearly who is your customer persona. In other words, who are your customers (or who do you think they will be)? Which gender, age range, social background, interests, etc?
Where are you going?
The third section of the company description should explain what your strategy is in the short to long term. Are you expecting to launch new products? To expand regionally, internationally? Etc.
3. Market plan and analysis
The market plan and analysis section tell investors and lenders that you have extensively studied the market and reveal your competitive plan.
Your market plan and analysis section should include the following:
Industry overview and outlook
Here you need to clearly identify 2 very important metrics:
- Market size: how big is your market?
- Market growth: how fast does your market grow?
If you are operating in a niche market, chances are that you will face some challenges: the information might not be publicly available. In any case, you should be able to make a high-level estimation of your market. Read our article on market sizing and how to estimate TAM, SAM and SOM for your startup.
When looking for these metrics, you have multiple sources of information: public reports, specialised press, etc. Even public companies publish press releases and annual reports including some of their proprietary market estimates so be sure to look there too.
Competitive landscape
Here we must answer 2 key questions:
How fragmented is your market?
Are there 3 big players sharing 90% market share or thousands of small players? Here, refer to public market reports and your own understanding of the competitive landscape.
A few questions you could ask yourself, among others:
- Who are your competitors?
- Are they local, regional, national or global?
- Are there any product alternatives to your product?
- What about their IP / technological advantage?
Where do you position yourself vs. competition?
Is your solution a game changer other competitors don’t have (yet)? Do you have competitors with similar products/services?
Ideally, you would create a small table with, for each type of competitors and their main characteristics.
For instance, do they all a global presence? Do they cover all the products you offer? What is their relative price positioning (expensive vs. accessible)?
4. Organization and management
The amount of details you need to include here varies depending on the size of your company.
No matter how many leadership roles there are, an organizational chart effectively shows lenders and investors how the management system is structured.
If you plan on running your business alone indefinitely, you can write a short paragraph explaining your qualifications and previous professional experiences.
The first thing you should include in this section is a list of each management position. This list includes who will fill the role and the qualifications of these people. These people are the heart of your company, and their skills and experience are vital in ensuring your company’s success.
Next, provide any additional information about how the management team will contribute to the business’s success. Be sure to give as many details as possible since lenders need to be comfortable and confident that you have a good team running your business.
Lastly, include information about the Board of Directors (and/or any other advisors to your business).
5. Service or product line
The level of detail and the content of this section changes depending on the type of business you have. A number of questions you need to answer are shown below (but not limited to):
- Are you selling products or services (or both)?
- How many products do you sell?
- What are they?
- What is their pricing?
- How do they work?
- Are your products protected by any kind of intellectual property (copyright, patent, etc.)?
- If you do not manufacture all of your product(s): who are they suppliers? Where do they fit in the value chain? etc.
6. Marketing and sales
Your SBA business plan template should include a marketing and sales plan where you describe your strategy for acquiring potential clients.
Here, you should give details about your marketing plan. A few questions you should answer are:
- How you plan to build and support your sales strategy?
- What channel(s) are you using (online vs. offline)?
- How it makes sense for your target audience (the customer persona mentioned above)?
What about your metrics?
Sales and marketing goals and KPIs are also provided in this section. Don’t forget to include a detailed report about budgets for both sales and marketing.
Include metrics such as conversion rate, customer acquisition cost (CAC), the efficiency of your sales team, etc.
It’s ok if you don’t know them already (if you are about to launch you new venture for example), yet you should have at least targets for them. How many website visitors do you expect to generate next year? What is your target conversion rate? Etc.
This particular report would be of great interest to lenders since they will glimpse how you handle your budget. Indeed, if you expect to spend in average $100 Customer Acquisition Cost, lenders will tie the number into your financial projections later on (more on that below).
Proving lenders you are able to link your financial projections with your actual business metrics (customers, sales volume, etc.) is a big plus. Indeed, that way you will show lenders you understand very clearly your business and how it ties into your financials (more on that in our article on why you should build a solid financial projections).
7. Funding request
The funding request is the section of your SBA business plan template where you communicate to your investors how much you need.
This report also includes how you plan on repaying your loan. It’s also essential to explain how you plan to spend the funding you’ll receive for your business.
Will you spend the loan in working capital, in equipment, in inventory, salaries or marketing costs? The more specific you are, the better.
If you haven’t done so, we really recommend you read our article on how to determine how much you should raise for you business. While raising too little creates obvious problems, raising too much isn’t necessarily better.
On top of the amount, a good practice is to include a pie chart of where you will spend that money over a given period (your runway). Will you spend the bulk of it in product development to build your MVP? Or will you use a large portion in sales & marketing to commercialise your product and find product-market fit?
Our financial model templates include a cash burn dashboard where you can easily assess how much you should raise, and where you will spend your money. We also included charts ready to be included in your pitch deck. See how to use our cash burn dashboard here.
The funding request usually includes an overview of the business. You also have to outline how much funding you need for the next five years. The standard timeframe for repaying your loan is usually ten years, so lenders expect to see some success in your business by that time. Mention a detailed explanation of how the funds will be used and strategic financial plans for the future here. Include financial information for current operations if applicable.
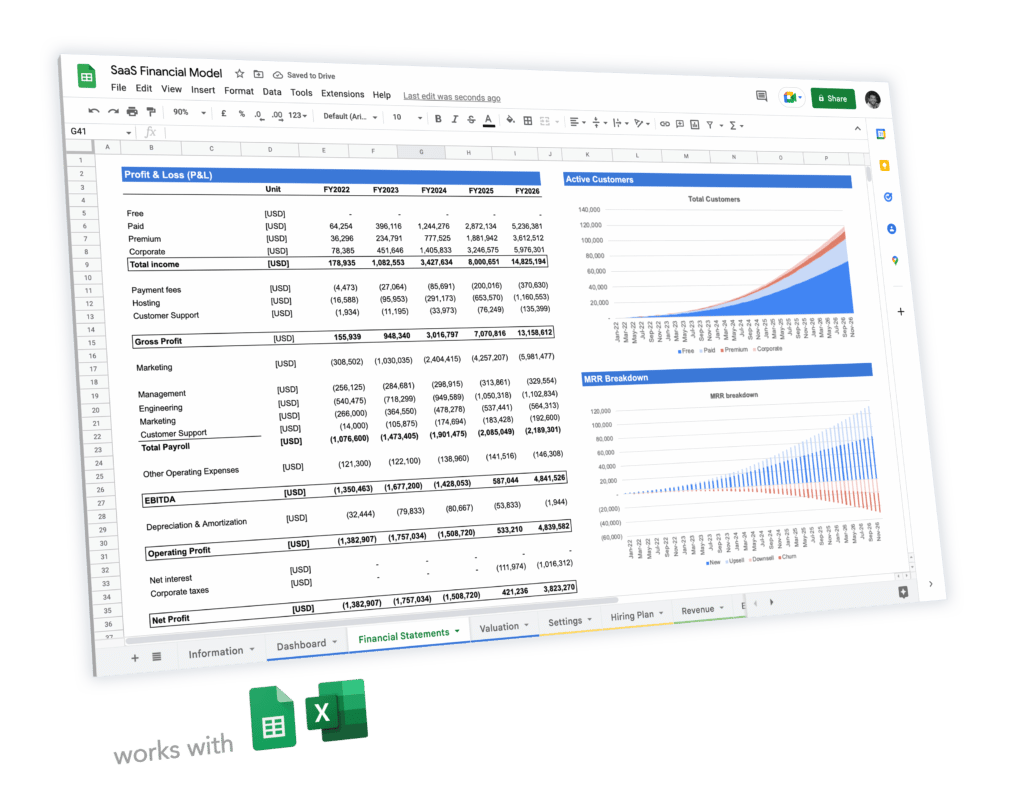
8. Financial projections
The financial projections section of your SBA business plan is one of the most important one.
Why? Lenders will have a thorough review of your expected financials over the next 3 to 5 years and judge whether your financial projections:
Are realistic (and use verifiable assumptions)
We are all by nature optimistic, especially when we are running businesses. It’s good to be optimistic, yet it is another one to be unrealistic.
Also, when presenting your financial projections, make sure to make it clear what are your assumptions. The more sources you can find to back up your forecasts, the better.
If you need help building realistic projections for your business, we have lots of free content. Make sure to check out our guides below:
- The 5 Mistakes To Avoid For Your Startup Financial Plan
- How To Build Realistic Revenue Projections For Your Startup?
Allow you to repay the SBA loan in the future
It’s great if you have built rock-solid and realistic financial projections for your business plan. Yet, if your plan doesn’t allow you to meet your debt obligations (the SBA loan and any other debt your business might have), lenders will not grant you any loan.
When assessing whether your financial plan allows you to repay the debt, you should check if the positive cash flows your business generates are enough to cover your debt repayment (and interests).
What financials should you include?
In short, you should present 3 different set of financials:
- Profit-and-loss
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
If you don’t know them already, these are the financial statements every business need to prepare at least annually (with the help of an accountant). For more information on what they are and how to prepare them, read our articles below:
- 4 Key Financial Statements For Your Startup Business Plan
- SBA Loan Application: 6 Steps To Build Solid Financial Projections
9. Appendix
This section is the best place to add supporting documents like charts, graphs, and data.
For example, a complete list of documents like licenses, contracts, maps, etc. makes you more attractive to lenders as it gives them more content to review. If you do so, make sure to reference the documents in appendix and link them to pages in earlier sections. Avoid using the appendix as a dump section: it should be well organised and structured (else no one will bother looking at it).

 5-year pro forma financial model
5-year pro forma financial model 20+ charts and business valuation
20+ charts and business valuation  Free support
Free support